Costing Techniques
Costing techniques are the approaches or principles used to appropriately present cost data and statement to the management for evaluation and/or decision making. The three common costing techniques are;
- Absorption costing
- Marginal costing
- Budgetary control costing
- Standard costing
Explanation
Absorption Costing
Definition; it is a practice/procedure of combining all the costs associated to a particular product during production process. The technique considers charging all types of costs, be it direct materials, direct labor, direct expenses and overheads on a particular product.
The procedure is that the direct costs is charged to the particular product and if there is any overhead, it is first charged to the cost Centre and then later absorbed to the cost unit.
The outlay with absorption costing approach appears as follows;
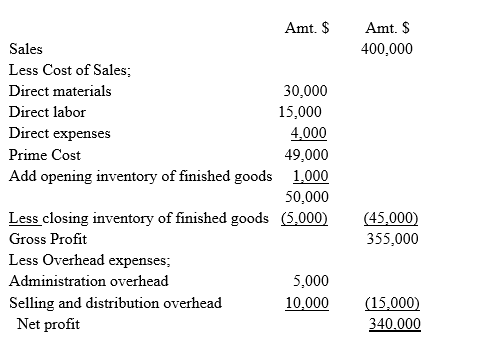
Therefore, the cost accountant presents the cost/ profit statement to the management in this structure for decision-making purposes.
Marginal Costing
Definition; it is a practice/procedure of ascertaining variable costs only which is affiliated to specific product or unit during production process. The technique considers charging all types of variable costs, be it direct materials, direct labor, direct expenses and overheads on a particular product as long as it is variable in nature.
The procedure is that the marginal costs is charged to the particular product and if there is any fixed overhead pertaining certain period of time, it is written off against the contribution of that period.
It is normally assumed that fixed costs remain constant and such costs does not affect the decisions of the management pertaining the production of alternative product.
The outlay with marginal costing approach appears as follows;

Budgetary Control
Definition; it is a technique of presenting costs and statement to the management in a manner that comparison is possible between departments or organizations. Hence, the technique entails presentation of both estimated and actual results of a department, a company or an organization. The resultant outcome is a deviation, which may favorable or unfavorable or a zero deviation. In all those circumstances, the management make well-informed decisions.
Standard Costing
Definition; Standard costing is a technique that involves presentation of cost data at predetermined value for each product which is compared with actual cost of the product to evaluate the performance of the firm. If the actual cost is less than the predetermined cost, it is a case of unfavorable results. Whereas, if the predetermined cost is more than the actual cost, it is a case of favorable results