Sunk Cost
Definition
Sunk cost is already economic resources consumed by the business before another decision is made. This is cost which has already occurred and cannot be relied upon to decide on the next level of production. This cost is classified so under the criterion of critical decision the management has to make. Sunk cost is an historical cost and unrecoverable. For example, insurance or investment of cash in a project. Such cost does not guide the decision maker to decide to produce an additional unit of a particular product in the future.
Circumstances Under Which Sunk Cost Arise
- When there is agency conflict
When the management acting on behalf of the owners of the company goes ahead and contrary serves their personal interest by divesting the cash resources in the wrong projects which stall in the future.
- Change in technology
When there is change in technology, some technologically affiliated assets or investments are rendered obsolete. Since they are no longer in use yet some cash was tied to the asset, this then turns out to be sunk cost.
- Asset breakdown
If an asset had been purchased for a particular purpose and by bad luck breaks down on usage, then the already spend cash on that asset is a sunk cost.
- Business closure or shutdown
When a business is operating under losses or it operates unlawfully hence forced to close down. Then it means that any asset acquired by the firm for any purpose will be brought to a standstill. As a result, the assets thereof become non-functional and this means the cash already spend to acquire the asset for the closed business becomes a sunk cost.
- Pandemics in a country
Any pandemic striking in an economy renders companies close down due to low economic performance. As a result, the assets already acquired stall up and become non-functional. This means the cash outflow associated to its acquisition is a sunk cost.
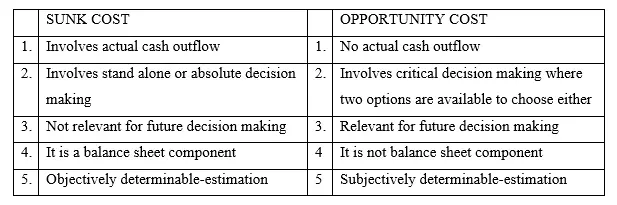
Table 1.1: Difference Between Opportunity Cost And Sunk Cost
Advantages Of Sunk Cost
- Can be accounted for in books of account as compared to opportunity cost.
With sunk cost, it is an actual cash out flow and hence put in watch. This helps in balancing the spending of the business.
- Help in raising subscription income
In some organizations such as not for profit making firms such as societies, they receive subscription in advance and this becomes a sunk cost as far as far as the members are concerned. But such a payment is a sunk cost to those who have paid it for they cannot be refunded in the normal circumstances.
- Used in budgeting
Since sunk cost is an historical cost in nature, this aspect of cost is used for budgeting purposes for the figures are used as benchmarks or points of reference when planning for the future.
- Sunk cost are associated with acquisition of income generating fixed assets
When sunk cost are incurred, most of the time they are costs affiliated with the acquisition of economically viable assets that help in income generation. For example, purchase of a posho milling machinery.
Disadvantages Of Sunk Cost
- The costs are irrecoverable
Once the cost is paid for, no recovery or one cannot reverse that transaction.
- Irrelevant to decision making
This type of cost is useless as far as making future decisions is concerned
 About the Author - Dr Geoffrey Mbuva(PhD-Finance) is a lecturer of Finance and Accountancy at Kenyatta University, Kenya. He is an enthusiast of teaching and making accounting & research tutorials for his readers.
About the Author - Dr Geoffrey Mbuva(PhD-Finance) is a lecturer of Finance and Accountancy at Kenyatta University, Kenya. He is an enthusiast of teaching and making accounting & research tutorials for his readers.