What is a general journal?
A general journal is a book of original entry where both cash and credit transactions of non-trading nature are recorded from the corresponding source document. It should be noted that, Purchases day book, Purchases returns book/Returns outward book, Sales day book and Sales returns book/Returns inward book are referred to specific journals and they are affiliated to recording of trading transactions. However, for the case of general journal, as the name suggests, it is used for general transactions and other functions. When recording transactions in a general journal, we say we are journalizing. General journal has four columns where by the first column is for date, then followed by details, then a DR and CR column as shown herein
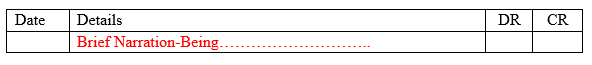
After recording (ie journalizing) a transaction in a general journal, a brief explanation/narration is added to describe the nature of transaction. The narration should be framed as follows: “Being…….”.
Functions/uses of general journal
The following are the functions of general journal;
-
Determination of opening and closing entries of accounts especially when there is a missing item of the balance sheet
-
Posting of transactions to the respective ledger accounts.
-
Cash or credit purchases and/or sales of non-current assets on credit.
-
End of year adjustments
-
Correction of errors.
Example of a general journal
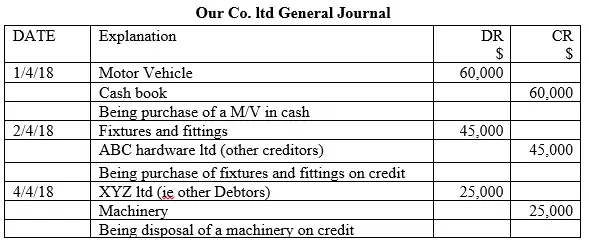
Our Co. ltd carried out the following transactions in the month of April, 2018
2018, April 1st bought motor vehicle in cash $60,000
2nd purchased fixtures and fittings $ 45,000 on credit from ABC hardware ltd
4th sold machinery for $25,000 on credit to XYZ ltd
Required
Record the transactions to the respective general journal
Solution
Summary
Part one/beginner level of this tutorial series has justified why you as an entrepreneur/ learner need to build your trust and appreciation of the Accountancy knowledge you have acquired. You have known the advantages of having Financial Accounting tips for it aids in improving your managerial skills. Part one has also established the point of detail as far as recording of business transactions are concerned. In level one of this series, transactions were simply recorded in the respective ledger accounts and then determination of profit or loss was established. In this part one of level two of the tutorials, it has been brought to light that accounting cycle is broader and of in depth than what entrepreneurs imagine. Part one has made you appreciate the role of source documents and books of original entry and justifies the reason why as an entrepreneur, you need such documents rather than carelessly recording your business transactions straight away to ledger accounts. Some of the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) has been applied which I believe they are an eye opener for the thriving of your business.
Part one has also aided you on how to prepare the relevant documents in every stage of business deals, be it cash or credit transaction. You have realized that shifting of information from the source documents to the books of original entry is referred to as “to transfer” and not posting for the principle of double entry does not apply. Contrariwise, if you are shifting the information in the books of original entry to the respective ledger accounts, the term “posting” is used for it involves use of double entry principle whereby as you credit one account you must make a corresponding debit entry in another account and the vice versa is true.
Part two/intermediate level has revealed to you that, although we have diverse categories of books of original entry, cash book is a unique one for it serves as both a book of original entry and a ledger account. Also, a cash book is used to record cash transactions only although those transactions of credit nature end up being recorded herein. Further, cash book accommodates unique transactions such as cash discounts, contra entry transactions and petty cash book transactions.