Applied research: definition, methodology, methods, characteristics, examples and advantages
1.1 Definition
What is Applied Research? This is a type of research which is Classification under Usage of research and it involves a systematic or step by step investigation on how to practically solve a research problem which can be either societal, educational, political or economical in nature as discovered by Basic Research.
It should be noted that Applied research uses empirical methods, such as experiments for the purposes of data collection in the domain of the researcher’s interest. The research findings carry a solution to the research problem at hand hence it is immediately implemented once the research is complete. Since Applied Research is solution based, it is therefore further classified in to;
Action Research
Evaluation Research
Research and Development
Action Research: It is sub-category of Applied Research which assist organizations with guidelines on how to solve problems related to their operations.
Evaluation Research: It is a sub-category of Applied Research which assists in analyzing of existing information to help the interested parties make decision from well informed platform.
Research and Development: It is a sub-category of Applied Research which assist in establishment of new products or goods/services for a specific market.
Applied research methodology
2.1 Definition
Applied Research methodology involves choosing a logical procedure on the research problem to be practically solved which may involve identification of specific objectives, research hypothesis and identification of research gaps to be fulfilled. It also entails the methods used in identification of the study population and sample size determination, type of data to be collected and how it will be collected and analyzed, data presentation and interpretations thereof and then implementation of the research findings.
The aforementioned description /definition on Applied Research methodology is in line with Kothari (1984) who assumed that research methodology is the rationality behind the methods we use in the context of our research study. This provides a foundation as to why one is using a particular technique or procedure at a particular stage in the research process and not others so that research output is accomplished successfully.
2.1.1 Questions Applied Research Methodology tries to Answer
This type of research is solution driven investigation and this time round, unlike other types of research, there is no question to be answered but it is a matter of providing an immediate solution the problem at hand.
Some of the Applied Research Scenarios that exists are such as;
Solution to increase in crime level in Houston slums
Solution to decrease of market share for toddler clothes
Solution to decrease of academic performance level in secondary schools
Solution to increase of cancer cases amongst married women
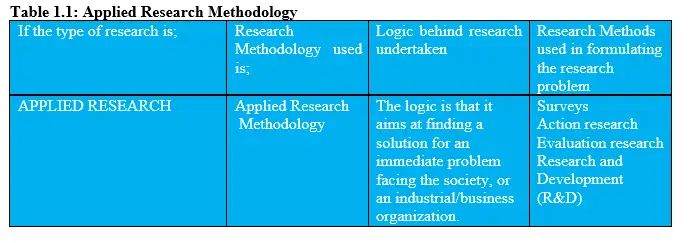
The following matrix portrays the link between Applied type of Research and the type of research methodology adopted and then an explanation of the logical approach associated with this category and then in the last column, the research method(s) used in formulating the research problem as indicated in Table 1.1
2.2 Applied Research Methodology-Diagrammatic Approach
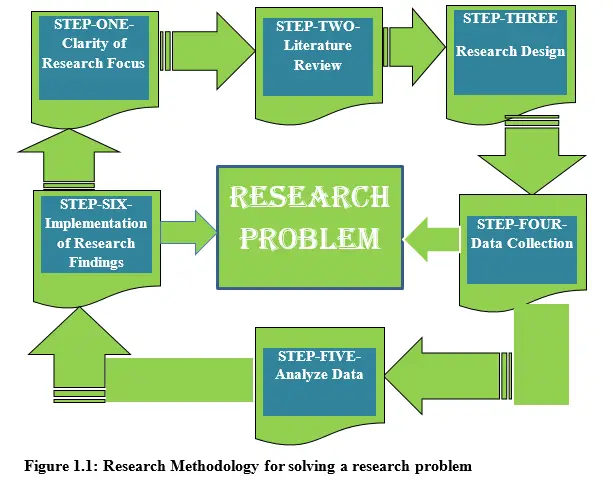
The following diagram represents a summary of logical roadmap to be adhered to in Applied research methodology
2.3 Logical Steps; Applied Research Methodology
The following logical steps describe the Applied Research methodology. From step one to six, it represents a logical way of how systematically the matter at hand need to be dealt with. Remember that in this approach, the researcher aims at providing an immediate solution to the research problem.
STEP-ONE-Clarity of Research Focus
In step one, the researcher initiates the research process by asking himself or herself some specific question or internalize on the research question at hand such as;
What does the researcher know about the matter or situation?
What is that the researcher does not know about the situation?
What is the goal of the research to be achieved at the end of the day?
STEP TWO- Literature Review
To get more insight on the research question or problem, literature review is undertaken to access information from the existing data bank such as results gotten from the Basic Research.
STEP-THREE-Research Design
After reviewing the information, research design is necessary so as to identify the method to use to collect data. The method used for Applied Research are interview, survey, focus group, and observation.
STEP FOUR-Data Collection
Step four entail the actual data collection which utilizes the aforementioned approaches in step three. Since this type of research is supposed to end with practical solutions to the end users, the researcher needs to ask him/herself the following questions;
How do I improve on efficiency and effectiveness in an optimal manner?
How do I ensure that the data collected is sensible to the subject matter ahead?
How do I set a working or plausible recommendations for my end users?
STEP-FIVE- Analyze Data
In this step, the researcher analyses the data so as to realize the research findings ready for use.
STEP-SIX-Implementation of Research Findings
The final step is that of dissemination of the research findings and implementation. That is, a summary of the findings in a report form is presented to the end users or the stakeholders.
Applied research methods
3.1 Definition
Research methods are all the techniques that are utilized in all the stages of research processes. They are tools used to ensure the end results of research task are accomplished. These techniques vary from one stage of research process to another. These methods are further classified in to two categories, namely;
- a) Pre-Data analysis methods
- b) Data Analysis related methods
As per Table 1.1 in this article, the applied research methods indicated in that table (refer), namely Surveys, Action research, Evaluation research and Research and Development (R&D) methods are for the purposes of formulating the research problem and are some of the methods which fall under pre-data analysis category. However, in this discussion of applied research, we will focus first on the FOUR main methods of data collection which are also pre-data analysis in nature. That is; Interview, Survey/ Questionnaire Data Reporting and Observation.
Data collected under Applied Research is of both qualitative and quantitative in nature. On top of the data collected, the researcher further undertakes experiments to achieve the set goal.
Data accumulation methods followed while conducting applied research are provided below
1. Interview
Interviews are carried out with the specific interviewee who is expected to provide the relevant information for the solution needed. The nature of the interview is on one-on-one basis. In some cases, digital cameras, camcorders and audio recorders are made use of so as to correctly capture the right data.
2. Survey/ Questionnaire
Data is also collected from the respondents using survey/questionnaire approach which involves accumulating responses from the unit of observations relied upon.
3. Data Reporting
Data is also acquired by relying on public domain sources such as websites, journals, magazines and newspapers. The information gathered has to be relevant to the topic under investigation. Sometimes this approach is faced by some challenges such as biasness either from the researcher’s or respondent’s side.
4. Observation
Observation is an empirical approach which is less bias in data collection for it involves straight away physical watching of unit of observation to collect the information needed.
Characteristics of applied research
Primary theme of this research is to provide practical solution to an immediate problem
- Empirical based
- Advocates for accuracy in observation and description
- Heavily relies on Basic Research results.
- Analytical in nature.
Advantages of applied research
- Provides immediate solution to a firm in an empirical manner.
- Unlike other types of research, it is not subject to human biasness for it is objective for it uses empirical approach
- It saves the financial resources of the organization for guiding the management to make well informed decisions
- Help organization in advancement in innovation such as introduction of new products in the market
- Help in creation of an additional new objectives.
Disadvantages of applied research
- It is not flexible in nature as it is restricted to a stipulated deadline.
- It does not advocate for generalization of research findings as it is in the case of Basic Research.