Capital Expense
Capital expense is the cash outflow paid by the business to a third party as a result of the former (the business) receiving some services during the Extra-ordinary or abnormal way of doing business.
Key Words
- Cash outflow-for a business expense to be classified as so, there must be an actual cash outflow involved. In other words, the business uses its cash or non-cash resources to pay out for the services provided.
- Third Party-the payment is made to a third party means somebody or persons being paid does not own the business in anyway. In other words, he is an outsider to the business. for example employees or a contractor. This is the reason why dividends paid to common shareholders are not business expense although there is actual cash outflow from the business for the common shareholders are insiders. They are the owners of the business and that again is why such payment of dividends is referred to as profit and loss appropriations but not business expense.
- Provision of services-the rationale behind the payment is in exchange of services provided to the business by the third party such as employee related services such accountant services, human resource services and security services. Also other services may include transport, airtime, insurance, advertisement, rent and rates and electricity. Just to mention but a few
- Abnormal operations of the business-the expense being paid for should be as a result of an activity far away from what is stated in the object clause. All other activities excluded in this object clause are extra-ordinary business activities. So any expense such as purchase of a non-current asset, falls under capital expenditure.
This implies that any purchase of a non-current asset which is not meant for re-selling falls under capital expense and that is an abnormal operation.
Advantages of Identification of Capital Expense
- Aid in management decision making-with ability to identify capital expense helps much for the management is able to tell the level of asset tangibility and the corresponding revenue generation to assess on the correlation between the two so as to know the productivity efficiency thereof.
- Help during the preparation of comprehensive income statement. The identification of the capital expenditure avoids understating the net profit of the business which in turn will adversely affect the tax liability thereof.
- Help in separation of debtors of the company. Identification of debtors related to purchase of non-current assets on credit results to creation of “other debtors” contrary to trade debtors. This approach of separating the two types of debtors helps in ensuring that the debtors for non-current assets such as inventory are not mixed up resulting to exaggeration of trade debtor values or making of wrong payments.
- Assigning of the right provisions. Both trade debtors and other debtors originating from purchase of non-current assets on credit have provisions attached to them. Ie trade debtors have provision for doubtful debts and non-current assets are assigned provision for depreciation. Identification of the capital expense, translating to non-current assets reduces the probability of mixing the charges at the end of the financial period.
- Help in preparation of Properties Plants and Equipment (PPE) schedule. With identification of the capital expense, it becomes easy to capture all the cost elements associated with PPE whether an asset was purchased on cash or on credit
Disadvantages of Identification of Capital Expense
1. Cumbersome -it is not easy to identify the cutting line of capital and revenue expenses especially if the business is a small one like small and medium enterprises.
2. Identification of capital expense is not universal to all firms in the same industry. So, it is not easy to compare the size of the firm using total asset base.
3. Requirement of qualified accounting officers-the activity of doing the classification is sensitive and not every accounts affiliated officers can do the classification. Therefore, the business is required to engage somebody who is properly qualified.
Accounting Treatment of Capital Expenses
Capital expenses are cash outflows from the business paid to a third party during the abnormal or extra-ordinary operations of the business. The accounting treatment of capital expense as follows;
a)If cash purchase of non-current asset takes place
b)If credit purchase of the non-current asset takes place
a)In case of cash purchase of non-current asset
If the business pays its capital expense in time, the accounting entries will be as follows;
On payment of cash for the full price of the capital good or non-current asset
Journal entry

Example 1
1st/12/2018, JKL co ltd purchased office equipment of $10,000 and paid the amount by check.
Required
i) Journalize that transaction as on 1st/12/2018
ii) Post the transaction in the respective ledger accounts
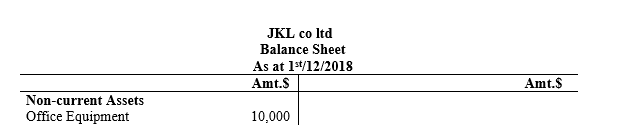
iii)Show the accounting treatment of this transaction in the balance sheet/ statement of financial position of JKL co ltd as on 1st/12/2018
SOLUTION
NB: That purchase of a non-current asset is a case of extra-ordinary activity for the main aim of acquisition is not for re-selling to make profits although disposal of a non-current asset can result to capital gain/profitability.
Therefore,
i)Journal entry is as shown herein.

ii) Posting to respective ledger accounts
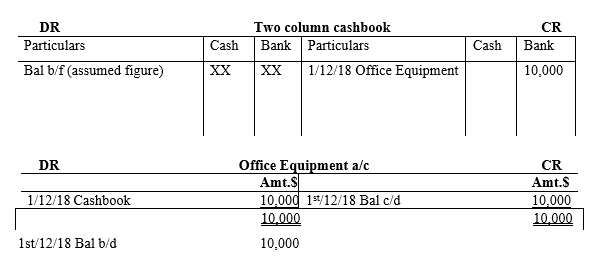
iii) Balance sheet
b)In case of credit purchase of the non-current asset
Example 2
Suppose 1st/12/2018, JKL co ltd purchased the same office equipment of $10,000 on credit from USA Equipment suppliers ltd
Required
i) Journalize that transaction as on 1st/12/2018
ii) Post the transaction in the respective ledger accounts
iii)Show the accounting treatment of this transaction in the balance sheet/ statement of financial position of JKL co ltd as on 1st/12/2018
SOLUTION
NB: That purchase of a non-current asset is a case of extra-ordinary activity for the main aim of acquisition is not for re-selling to make profits although disposal of a non-current asset can result to capital gain/profitability.
Therefore,
Journal entry is as shown herein.

ii) Posting to respective ledger accounts

iii)Balance sheet

 About the Author - Dr Geoffrey Mbuva(PhD-Finance) is a lecturer of Finance and Accountancy at Kenyatta University, Kenya. He is an enthusiast of teaching and making accounting & research tutorials for his readers.
About the Author - Dr Geoffrey Mbuva(PhD-Finance) is a lecturer of Finance and Accountancy at Kenyatta University, Kenya. He is an enthusiast of teaching and making accounting & research tutorials for his readers.